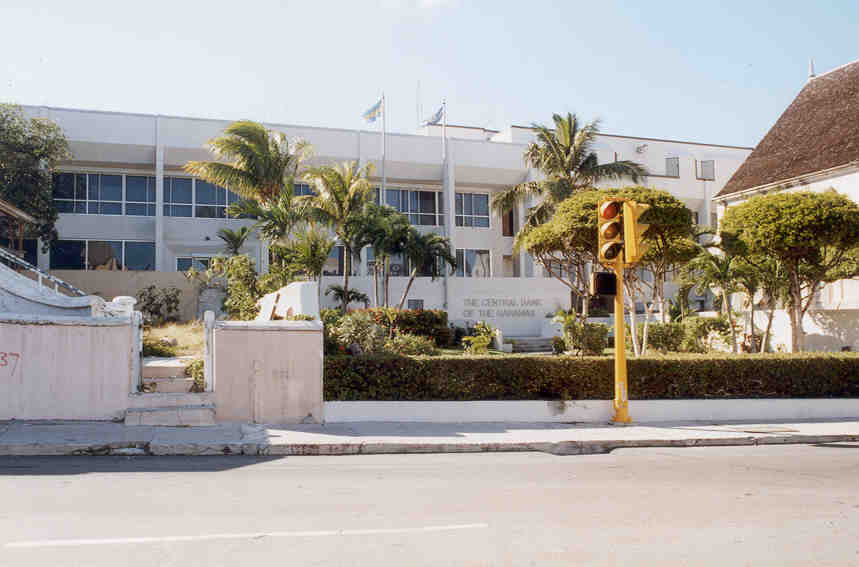
The Central Bank of The Bahamas was established on June 1, 1974 under the Central Bank of The Bahamas Act, 1974. Its predecessors are The Bahamas Monetary Authority, which was created in 1968, and the Commissioner of Currency Board, which was established in 1919. The functions of the Monetary Authority included the issue and redemption of currency, supervision of banks and trust companies operations; and administration of exchange control. It was also the custodian of the country's international reserves. The Currency Board was essentially an administrative unit whose function was limited to the issuance and redemption of local currency against the pound sterling at par.
The Central Bank of The Bahamas was established on June 1, 1974 under the Central Bank of The Bahamas Act, 1974. Its predecessors are The Bahamas Monetary Authority, which was created in 1968, and the Commissioner of Currency Board, which was established in 1919. The functions of the Monetary Authority included the issue and redemption of currency, supervision of banks and trust companies operations; and administration of exchange control. It was also the custodian of the country's international reserves. The Currency Board was essentially an administrative unit whose function was limited to the issuance and redemption of local currency against the pound sterling at par.
Other Local Financial Institutions
The term 'other local financial institution' refers to all resident banks and/or trust companies other than the commercial banks. Most of the other local financial institutions are involved in trust business. Some of the services they provide include acting as trustees to pension funds and as executors or administrators to the estates of deceased persons.
Trust Companies
The primary function of a trust company is to act as trustee, fiduciary or agent for individuals or firms in a variety of capacities, such as administering trust funds(including their investments) executing wills, acting as custodian for property held in trust, etc. Many trust companies also perform some banking functions, such as, accepting deposits and making loans.
A nominee trust company is a company which holds securities and other assets in its name on behalf of clients of its parent bank or trust company.
Some trust companies are licensed to engage in both trust and banking activities. On the banking side, the proportion of Bahamian dollar business of these companies has been traditionally small, as the majority of their transactions are in foreign currency.
Insurance Companies
The Insurance Act 1969 provides basic protection for the public in its dealings with local insurance operations. It contains provisions governing the registration and cancellation of registration of insurance agents, brokers and salesmen. No person can carry on any insurance business in or from within The Bahamas unless he/she is registered. The Act is administered by the Registrar of Insurance Companies who is responsible to the Minister of Finance. The function of this office is to regulate, inspect, licence and control insurance companies, agents, brokers and salesmen.
There are three categories of insurance operations in The Bahamas :
- Life
- Life and other than life
- Other than life
There are five types of life policies:
- Term
- Whole Life
- Endowment
- Industrial Life
- Group Life
Other than life policies offer coverage for loss of or damage to property; accident and sickness; and other health-related problems.
Captive Insurance
A captive insurance company is an offshore insurance and reinsurance company formed and owned by a parent organization. The main function of a captive insurance company is to insure and reinsure the existing risks of its parent company or the parent's and affiliate branches.
The major advantages of a captive insurance company is that it is able to insure various risks common to the parent company, which traditional insurance companies either refused to insure or insure at an unreasonably high rate.
View the following links for further details:
Commercial Banking / Private Banking / Other Local Financial Institutions / Captive Insurance
Source: The Central Bank of The Bahamas
-
 Public Consultation on The Draft Pension Bill, 2023See details...
Public Consultation on The Draft Pension Bill, 2023See details... -
 Vacancy Notice - Public ProsecutorsSee details...
Vacancy Notice - Public ProsecutorsSee details...
- Overview of the Financial Sector (this page)